
The Incoterms is an abbreviation for “International Commercial Terms.” This term represents a very useful way of communication and it’s actually aimed at reducing confusion between buyers and sellers. So, what is an incoterm? An incoterm represents a universal term that defines a transaction between importer and exporter so that both parties understand the tasks, costs, risks, and responsibilities, as well as the logistics and transportation management from the exit of the product to the reception by the importing country. Incoterms are all the possible ways of distributing responsibilities and obligations between two parties. It is important for the buyer and seller to pre-define the responsibilities and obligations for the transport of the goods.
They are a set of rules published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), which relate to International Commercial Law. According to the ICC, Incoterms® rules provide internationally accepted definitions and rules of interpretation for most common commercial terms used in contracts for the sale of goods’. All International purchases will be processed on an agreed Incoterm to define which party legally incurs costs and risks. Incoterms® will be clearly stated on relevant shipping documents.
Here are the overview of Incoterms® 2023 for 11 Terms.
· Ex works is when the seller places the goods at the disposal of the buyer at the seller's premises or at another named place (i.e., works, factory, warehouse, etc.).
· The seller does not need to load the goods on any collecting vehicle. Nor does it need to clear them for export, where such clearance is applicable, but they have to provide the documents for customs declaration.
· The seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the buyer at the seller's premises or another named place.
· The parties are well advised to specify as explicitly as possible the point within the named place of delivery, as the risk passes to the buyer at that point.
· The seller delivers when the goods are placed alongside the vessel (e.g., on a quay or a barge) nominated by the buyer at the named port of shipment.
· The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the products are alongside the ship. The buyer bears all costs from that moment onwards.
· The seller delivers the goods on board the vessel nominated by the buyer at the named port of shipment or procures the goods already so delivered.
· The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the products are on board the vessel. The buyer bears all costs from that moment onwards.
· The seller delivers the goods on board the vessel or procures the goods already so delivered.
· The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the products are on board the vessel.
· The seller must contract for and pay the costs and freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination.
· The seller delivers the goods on board the vessel or procures the goods already so delivered. The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the products are on the ship.
· The seller must contract for and pay the costs and freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination.
· The seller also contracts for insurance cover against the buyer's risk of loss of or damage to the goods during the carriage.
· The buyer should note that under CIF the seller is required to obtain insurance only on minimum cover. Should the buyer wish to have more insurance protection, it will need either to agree as much expressly with the seller or to make its own extra insurance arrangements.
· The seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the seller at an agreed place (if any such site is agreed between parties).
· The seller must contract for and pay the costs of carriage necessary to bring the goods to the named place of destination.
· The seller has the same responsibilities as CPT, but they also contract for insurance cover against the buyer's risk of loss of or damage to the goods during the carriage.
· The buyer should note that under CIP the seller is required to obtain insurance only on minimum cover. Should the buyer wish to have more insurance protection, it will need either to agree as much expressly with the seller or to make its own extra insurance arrangements.
· The seller delivers when the goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the named place of destination.
· The seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to the named place.
· DPU replaces the former Incoterm® DAT (Delivered At Terminal). The seller delivers when the goods, once unloaded are placed at the disposal of the buyer at a named place of destination.
· The seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to, and unloading them at the named place of destination.
· The seller delivers the goods when the goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer, cleared for import on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the named place of destination.
· The seller bears all the costs and risks involved in bringing the goods to the place of destination. They must clear the products not only for export but also for import, to pay any duty for both export and import and to carry out all customs formalities.
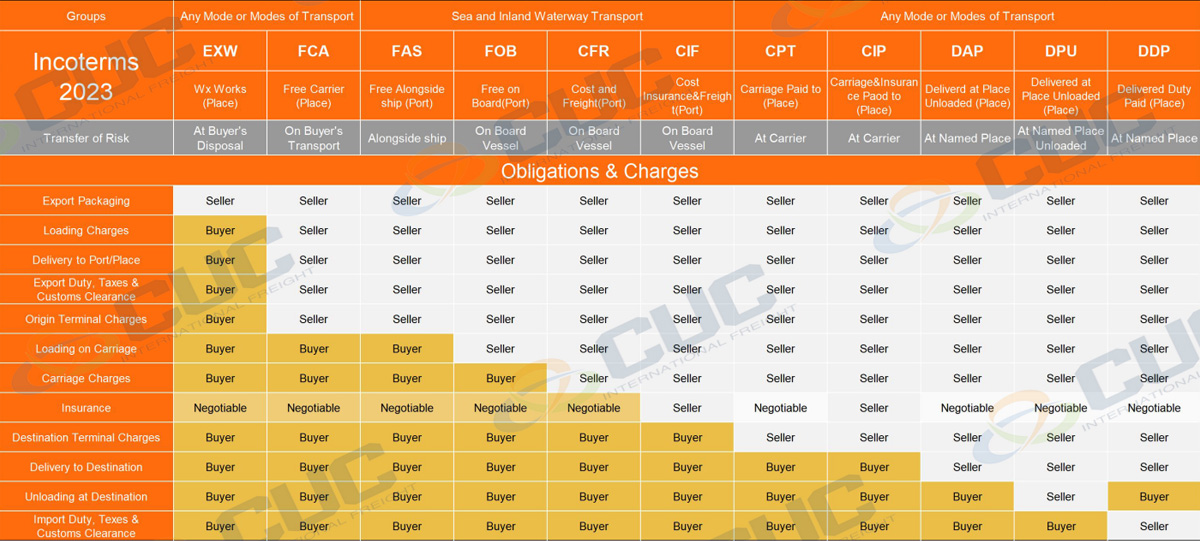
Chart showing Incoterms
Note: The content of this article and chart is only for general information purposes and shall not in any circumstances be considered bespoke legal advice or professional advice.
 The U.S. Import Bonds (Customs Bond)May 25, 2024Successfully to import products into the USA is a complex multi-step process. Customs clearance is very important part of process. When we comes to customs clearance, we have to refer to bonds. Custom...view
The U.S. Import Bonds (Customs Bond)May 25, 2024Successfully to import products into the USA is a complex multi-step process. Customs clearance is very important part of process. When we comes to customs clearance, we have to refer to bonds. Custom...view_400x400.webp) Door-to-Door Air Freight Hacks: How I Slashed China-US Shipping Costs by 28%March 24, 2025Slash China-US air freight costs 28% with hybrid logistics hacks. Real-case tactics: air ship chips + sea freight packaging, beat customs traps.view
Door-to-Door Air Freight Hacks: How I Slashed China-US Shipping Costs by 28%March 24, 2025Slash China-US air freight costs 28% with hybrid logistics hacks. Real-case tactics: air ship chips + sea freight packaging, beat customs traps.view What Is a Shipping Quote?September 28, 2025A shipping quote is a formal cost estimate provided by a freight forwarder, carrier, or logistics provider that outlines the total charges involved in moving goods from the origin to the destination. ...view
What Is a Shipping Quote?September 28, 2025A shipping quote is a formal cost estimate provided by a freight forwarder, carrier, or logistics provider that outlines the total charges involved in moving goods from the origin to the destination. ...view Shipping Rates Surge Less Than 24 Hours After Tariff Cuts AnnouncedMay 14, 2025Based on recent market feedback, on May 12, 2025, the governments of China and the United States reached an agreement to mutually reduce tariffs, aiming to ease trade tensions. However, major shipping...view
Shipping Rates Surge Less Than 24 Hours After Tariff Cuts AnnouncedMay 14, 2025Based on recent market feedback, on May 12, 2025, the governments of China and the United States reached an agreement to mutually reduce tariffs, aiming to ease trade tensions. However, major shipping...view